What is Gravitational Force?
The force of attraction between any two or more objects in the universe is called the gravitational force. And the process is called gravitation.
Newton gave a rule in 1887 for the relation between the factor effect on the gravitational force and the process of measuring such force, which is called Newton's universal law of Gravitation.
According to the above rules given by Newton, “The gravitational force generated between any two objects in the universe is directly proportional to the product of the mass of those objects and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centers of those objects.”
 |
| Gravitational force value of earth |
Before the 17th century, it was believed that the earth was at the center of the universe and the sun, moon and other planets are revolved around it. This is called geocentric theory. After then, according to heliocentric theory, the Sun is the center of the universe and all the planets and satellites revolve around it.
Soon after, Newton began researching it. According to Newton, not only does the earth attract ripe fruit or the moon, but all the objects in the universe attract each other. The process by which one massive particle attracts other massive particles is called gravitation.
For gravitational force examples, the earth attracts the moon and the moon attracts the earth. The effects of large bodies appear to have been felt in small bodies, but the effects of small bodies appear to be relatively small in large bodies.
The Earth attracts its only one satellite, the Moon, other planets and stars. It is also called gravitationalforce of earth.
What is Newton's universal Law of Gravitation?
“The gravitational force generated between any two objects in the universe is directly proportional to the product of the mass of those objects and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centers of those objects.”
 |
| law of gravitation |
Then according to Newton's universal Law of Gravitation,
F µ m1xm2 ………………. (i) (If d is stable)
F µ 1/d2 ……………………. (ii) (If m1 and m2 are stable)
Writing both relationships together
F µ
(m1xm2)/d2
or F = G(m1xm2)/d2 …………………. (iii)
The equation (ii) shows the gravitational force formula where 'G' is a constant, which is also called Universal Gravitational constant. The value of G is 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2. The value of 'G' has been discovered by Henry Cavendish with the help of sensitive balance.
The gravitational force formula
F = G(m1xm2)/d2 is the gravitational force formula. In this formula, if we keep the values of m1 = 1kg, m2 = 1kg and d = 1m, then F = G.
Therefore, the gravitational force is the Universal gravitational constant when two objects weighing 1 kg are placed at a distance of 1 meter.
It does not depend on mass, distance and medium (rare or denser) between bodies, so it is called universal gravitational constant.
The gravitational force generated between two objects differs in the following cases
1. 1. In case the distance is constant but the mass has changed
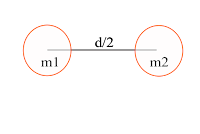
 Suppose A and B
are bodies, A has a mass of m1 and B has a mass of m2 and the central distance
between them is d and the force of attraction is F.
Suppose A and B
are bodies, A has a mass of m1 and B has a mass of m2 and the central distance
between them is d and the force of attraction is F.
According to Newton's universal Law of Gravitation
Now keep the distance between A and B constant
And Keep the mass of B twice.
F1
= G (m1x2m2)/d2
or F1 = 2G (m1xm2)/d2
F1 = 2F
Therefore, when mass of one of the two objects is doubled, their force also doubles.
2. 2. In case the masses are constant but the distance has changed
Suppose A and B are bodies, A has a mass of m1 and B has a mass of m2 and the central distance between them is d and the force of attraction is F.
According to Newton's universal Law of Gravitation
F = G (m1xm2)/d2 ………………….. (i)
Now keep the masses of A and B constant
And half the distance between A and B.
F1
= G (m1xm2)/(d/2)2
or F1 = 4G (m1xm2)/d2
F1 = 4F
Therefore, when the distance between two objects is halved, the gravitational force between them increases four times.
According to both conditions we can say that the gravitational force depends on their mass and the distance between the bodies.
Gravitational force SI unit
F = G (m1xm2)/d2
or F = Nm2kg-2(kg x kg)/m2 (SI unit of G is Nm2kg-2, unit of mass is kg and unit of distance M)
So that, F = N
This means the gravitational force SI unit N (N means Newton).
Gravitational force value of the earth for the moon
The mass of the earth is 6x1024kg, the mass of the moon is 7.2x1022kg and the distance between the earth and the moon is 385,000.6 km.
Here, m1 = 6x1024kg
m2 = 7.2x1022kg
d = 385,000.6 km = 385,000.6 x 1000m = 3.8x108m
And
the value of G is 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2
If we using the gravitational force formula
Then,
F = G (m1xm2)/d2
= 6.67x10-11 (6x1024x7.2x1022)/( 3.8x108)2 (Units are not used to make calculations easier)
= (288.114x10-11+24+22)/14.44x1016
= (288.114x1035-16)/14.44
= 19.95x1019N
Therefore gravitational force between earth and moon is 19.95x1019N.
Gravitational force between sun and earth
The mass of the sun is 2x1030kg, the mass of the earth is 6x1024kg and the distance between earth and sun is 1.5x108km. The gravitational force can be extracted from the above process using the gravitational force formula.
The Gravitational force value of the sun for the earth is 3.56x1022N
Thanks so much for reading my article. Please follow us for a new article.












0 Comments
If You need any new topic related post, please comment us.